Veröffentlichungen (in Englisch)
-
Artikel in wissenschaftlichen Zeitschriften
-
Bücher und Sammelbände
-
Abschlussarbeiten
Siehe auch die Profile auf Publons,
Orcid oder
Google Scholar.
1. Artikel in wissenschaftlichen Zeitschriften
 | Protein-membrane interactions with a twist
Jordan Klein, Loréne Schad, Thérèse E. Malliavin, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Soft Matter, 21: 4336, 2025.
 | Conformational Space of the Translocation Domain of Botulinum Toxin: Atomistic Modeling and Mesoscopic
Description of the Coiled-Coil Helix Bundle
Alexandre Delort, Grazia Cottone, Thérèse E. Malliavin, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25: 2481, 2024.
 | Flexoelectric fluid membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Niloufar Abtahi, Lila Bouzar, Nadia Saidi-Amroun, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
EPL, 131(1): 18001, 2020. Siehe auch arXiv:2006.04475.
 | Isometric bending requires local constraints on free edges
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Math. Mech. Solids, 24: 4051, 2019. Siehe auch arXiv:1904.05855.
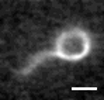 | Helical Superstructure of Intermediate Filaments
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, René Messina, Bernd Nöding, Sarah Köster, Hervé Mohrbach, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. Lett., 122: 098101, 2019. Siehe auch arXiv:1803.04691.
 | Vesicle dynamics in confined steady and harmonically modulated Poiseuille flows
Zakaria Boujja, Chaouqi Misbah, Hamid Ez-Zahraouy, Abdelilah Benyoussef, Thomas John, Christian Wagner, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Phys. Rev. E, 98: 043111, 2018. Siehe auch arXiv:1810.04500.
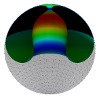 | Confining a fluid membrane vesicle of toroidal topology in an adhesive hard sphere
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
IOP Conf. Series: MSE, 186: 012021, 2017.
 | Squeezed helical elastica
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, Pierre Gosselin, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Eur. Phys. J. E, 39: 114, 2016. Siehe auch arXiv:1606.03611.
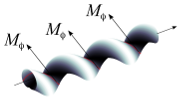 | How bio-filaments twist membranes
Julien Fierling, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Soft Matter, 12: 5747, 2016.
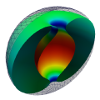 | Toroidal membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 92: 032721, 2015. Siehe auch arXiv:1509.00765.
 | Non-linear buckling and symmetry breaking of a soft elastic sheet sliding on a cylindrical substrate
Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 75: 115, 2015. Siehe auch arXiv:1503.05030.
 | Crunching Biofilament Rings
Julien Fierling, Martin Michael Müller, Hervé Mohrbach, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Europhys. Lett., 107(6): 68002, 2014. Siehe auch arXiv:1408.6787.
 | Confotronic dynamics of tubular filaments
Osman Kahraman, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Soft Matter, 10(16): pp. 2836-2847, 2014. Siehe auch arXiv:1312.3106.
 | Whirling skirts and rotating cones
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
New J. Phys., 15: 113055, 2013. Siehe auch arXiv:1306.2619.
 | Myotubularin and PtdIns3P remodel the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle in vivo
Leonela Amoasii, Karim Hnia, Gaëtan Chicanne, Andreas Brech, Belinda Simone Cowling, Martin Michael Müller, Yannick Schwab, Pascale Koebel, Arnaud Ferry, Bernard Payrastre, Jocelyn Laporte |
Abstrakt
J. Cell Sci., 126(8): 1806, 2013.
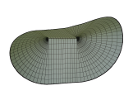 | Dipoles in thin sheets
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Osman Kahraman, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Eur. Phys. J. E, 36: 106, 2013. Siehe auch arXiv:1212.3262.
 | Fluid membrane vesicles in confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
New J. Phys., 14: 095021, 2012.
 | Petal shapes of sympetaleous flowers: the interplay between growth, geometry and elasticity
Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Miguel Trejo |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
New J. Phys., 14: 085014, 2012. Ausgewählt für die Highlights of 2012.
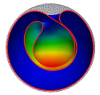 | Morphogenesis of membrane invaginations in spherical confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Europhys. Lett., 97(6): 68008, 2012. Siehe auch arXiv:1201.2518.
 | Conical instabilities on paper
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 45(1): 015203, 2012. Siehe auch arXiv:1107.5008.
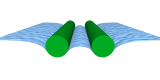 | Interface-mediated interactions: Entropic forces of curved membranes
Pierre Gosselin, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 83(5): 051921, 2011. Siehe auch arXiv:1011.1221.
 | Self-Contact and Instabilities in the Anisotropic Growth of Elastic Membranes
Norbert Stoop, Falk K. Wittel, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Hans J. Herrmann |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. Lett., 105(6): 068101, 2010. Siehe auch arXiv:1007.1871.
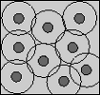 | Cell Model Approach to Membrane Mediated Protein Interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., 184: pp. 351-363, 2010.
 | Hamiltonian formulation of surfaces with constant Gaussian curvature
Miguel Trejo, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 42(42): 425204, 2009.
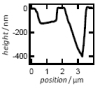 | Local Membrane Mechanics of Pore-Spanning Bilayers
Ingo Mey, Milena Stephan, Eva K. Schmitt, Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131(20): pp. 7031-7039, 2009.
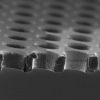 | Elasticity Mapping of Pore-Suspending Native Cell Membranes
Bärbel Lorenz, Ingo Mey, Siegfried Steltenkamp, Tamir Fine, Christina Rommel, Martin Michael Müller, Alexander Maiwald, Joachim Wegener, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Small, 5(7): pp. 832-838, 2009.
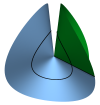 | Conical Defects in Growing Sheets
Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Jemal Guven |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. Lett., 101(15): 156104, 2008. Siehe auch arXiv:0807.1814.
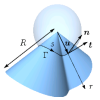 | How paper folds: bending with local constraints
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 41(5): 055203, 2008. Siehe auch arXiv:0712.0978.
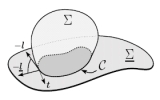 | Contact lines for fluid surface adhesion
Markus Deserno, Martin Michael Müller, Jemal Guven |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011605, 2007. Siehe auch cond-mat/0703019.
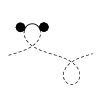 | Balancing torques in membrane-mediated interactions: Exact results and
numerical illustrations
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011921, 2007. Siehe auch cond-mat/0702340.
 | Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated
interactions
Benedict J. Reynwar, Gregoria Illya, Vagelis A. Harmandaris, Martin Michael Müller, Kurt Kremer, Markus Deserno |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Nature 447(7143): pp. 461-464, 2007.
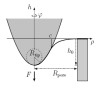 | How to determine local elastic properties of lipid bilayer membranes
from atomic-force-microscope measurements: A theoretical analysis
Davood Norouzi, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 74(6): 061914, 2006. Siehe auch cond-mat/0602662.
 | Mechanical Properties of Pore-Spanning Lipid Bilayers Probed by Atomic Force Microscopy
Siegfried Steltenkamp, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Christian Hennesthal, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Biophys. J., 91(1): pp. 217-226, 2006.
 | Interface mediated interactions between particles -- a geometrical approach
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstrakt
Weitere Informationen
Phys. Rev. E, 72(6): 061407, 2005. Siehe auch cond-mat/0506019.
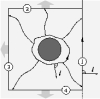 | Geometry of surface-mediated interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Soft interfaces can mediate interactions between particles bound to
them. The force transmitted through the surface geometry on a
particle may be expressed as a closed line integral of the surface
stress tensor around that particle. This contour may be deformed to
exploit the symmetries present; for two identical particles, one
obtains an exact expression for the force between them in terms of
the local surface geometry of their mid-plane; in the case of a
fluid membrane the sign of the interaction is often evident. The
approach, by construction, is adapted directly to the surface and is
independent of its parameterization. Furthermore, it is applicable
for arbitrarily large deformations; in particular, it remains valid
beyond the linear small-gradient regime.
 Wieder einklappen
Weitere Informationen Wieder einklappen
Weitere Informationen
Europhys. Lett., 69(3): pp. 482-488, 2005. Siehe auch cond-mat/0409043.
2. Bücher und Sammelbände
3. Abschlussarbeiten
-
Theoretische Untersuchungen von grenzflächenvermittelten Wechselwirkungen zwischen Kolloidteilchen, Diplomarbeit (2004).
-
Theoretische Untersuchungen zur Mechanik fluider Membranen, Doktorarbeit (2007).
-
Symmetry breaking in bioelasticity, Habilitationsschrift (2015).
|


