Publications
-
Articles in scientific journals
-
Books
-
Theses
See also profiles on Publons,
Orcid or
Google Scholar.
1. Articles in scientific journals
 | Conformational Space of the Translocation Domain of Botulinum Toxin: Atomistic Modeling and Mesoscopic
Description of the Coiled-Coil Helix Bundle
Alexandre Delort, Grazia Cottone, Thérèse E. Malliavin, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25: 2481, 2024.
 | Flexoelectric fluid membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Niloufar Abtahi, Lila Bouzar, Nadia Saidi-Amroun, Martin Michael Müller |
EPL, 131(1): 18001, 2020. See also arXiv:2006.04475.
 | Isometric bending requires local constraints on free edges
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
While the shape equations describing the equilibrium of an unstretchable thin sheet that is free
to bend are known, the boundary conditions that supplement these equations on free edges have remained elusive.
Intuitively, unstretchability is captured by a constraint on the metric within the bulk. Naïvely one would then
guess that this constraint is enough to ensure that the deformations determining the boundary conditions on these
edges respect the isometry constraint. If matters were this simple, unfortunately, it would imply unbalanced torques
(as well as forces) along the edge unless manifestly unphysical constraints are met by the boundary geometry. In this
article, we identify the source of the problem: not only the local arc-length but also the geodesic curvature need to
be constrained explicitly on all free edges. We derive the boundary conditions which follow. In contrast to conventional
wisdom, there is no need to introduce boundary layers. This framework is applied to isolated conical defects, both
with deficit as well, but more briefly, as surplus angles. Using these boundary conditions, we show that the lateral
tension within a circular cone of fixed radius is equal but opposite to the radial compression, and independent of
the deficit angle itself. We proceed to examine the effect of an oblique outer edge on this cone perturbatively
demonstrating that both the correction to the geometry as well as the stress distribution in the cone kicks in at
second order in the eccentricity of the edge.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Math. Mech. Solids, 24: 4051, 2019. See also arXiv:1904.05855.
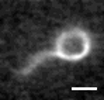 | Helical Superstructure of Intermediate Filaments
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, René Messina, Bernd Nöding, Sarah Köster, Hervé Mohrbach, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 122: 098101, 2019. See also arXiv:1803.04691.
 | Vesicle dynamics in confined steady and harmonically modulated Poiseuille flows
Zakaria Boujja, Chaouqi Misbah, Hamid Ez-Zahraouy, Abdelilah Benyoussef, Thomas John, Christian Wagner, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Phys. Rev. E, 98: 043111, 2018. See also arXiv:1810.04500.
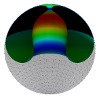 | Confining a fluid membrane vesicle of toroidal topology in an adhesive hard sphere
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
IOP Conf. Series: MSE, 186: 012021, 2017.
 | Squeezed helical elastica
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, Pierre Gosselin, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach |
Abstract
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 39: 114, 2016. See also arXiv:1606.03611.
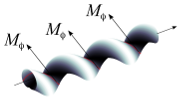 | How bio-filaments twist membranes
Julien Fierling, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Soft Matter, 12: 5747, 2016.
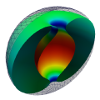 | Toroidal membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 92: 032721, 2015. See also arXiv:1509.00765.
 | Non-linear buckling and symmetry breaking of a soft elastic sheet sliding on a cylindrical substrate
Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 75: 115, 2015. See also arXiv:1503.05030.
 | Crunching Biofilament Rings
Julien Fierling, Martin Michael Müller, Hervé Mohrbach, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 107(6): 68002, 2014. See also arXiv:1408.6787.
 | Confotronic dynamics of tubular filaments
Osman Kahraman, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller, Igor M. Kulić |
Tubular lattices are ubiquitous in nature and technology. Microtubules and nanotubes of all
kinds act as important pillars of biological cells and the man-made nano-world. We show that
when prestress is introduced in such structures, localized conformational quasiparticles emerge and
govern the collective shape dynamics of the lattice. When coupled via cooperative interactions these
quasiparticles form larger-scale quasipolymer superstructures exhibiting collective dynamic modes
and giving rise to a hallmark behavior radically different from semiflexible beams.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Soft Matter, 10(16): pp. 2836-2847, 2014. See also arXiv:1312.3106.
 | Whirling skirts and rotating cones
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
New J. Phys., 15: 113055, 2013. See also arXiv:1306.2619.
 | Myotubularin and PtdIns3P remodel the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle in vivo
Leonela Amoasii, Karim Hnia, Gaëtan Chicanne, Andreas Brech, Belinda Simone Cowling, Martin Michael Müller, Yannick Schwab, Pascale Koebel, Arnaud Ferry, Bernard Payrastre, Jocelyn Laporte |
Abstract
J. Cell Sci., 126(8): 1806, 2013.
 | Dipoles in thin sheets
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Osman Kahraman, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 36: 106, 2013. See also arXiv:1212.3262.
 | Fluid membrane vesicles in confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 095021, 2012.
 | Petal shapes of sympetaleous flowers: the interplay between growth, geometry and elasticity
Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Miguel Trejo |
Abstract
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 085014, 2012. Also featured in the Highlights of 2012.
 | Morphogenesis of membrane invaginations in spherical confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 97(6): 68008, 2012. See also arXiv:1201.2518.
 | Conical instabilities on paper
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 45(1): 015203, 2012. See also arXiv:1107.5008.
 | Interface-mediated interactions: Entropic forces of curved membranes
Pierre Gosselin, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 83(5): 051921, 2011. See also arXiv:1011.1221.
 | Self-Contact and Instabilities in the Anisotropic Growth of Elastic Membranes
Norbert Stoop, Falk K. Wittel, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Hans J. Herrmann |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 105(6): 068101, 2010. See also arXiv:1007.1871.
 | Cell Model Approach to Membrane Mediated Protein Interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., 184: pp. 351-363, 2010.
 | Hamiltonian formulation of surfaces with constant Gaussian curvature
Miguel Trejo, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller |
Dirac's method for constrained Hamiltonian systems is used to describe surfaces of constant Gaussian curvature. A geometrical free energy, for which these surfaces are equilibrium states, is introduced and interpreted as an action. An equilibrium surface can then be generated by the evolution of a closed space curve.
Since the underlying action depends on second derivatives, the velocity of the curve and its conjugate momentum must be included in the set of phase space variables. Furthermore, the action is linear in the acceleration of the curve and possesses a local symmetry---reparametrization invariance---which implies primary constraints in the canonical formalism. These constraints are incorporated into the Hamiltonian through Lagrange multiplier functions, that are identified as the components of the acceleration of the curve. The formulation leads to four first order partial differential equations, one for each canonical variable.
With the appropriate choice of parametrization only one of these equations has to be solved to obtain the surface which is swept out by the evolving space curve. To illustrate the formalism, several evolutions of pseudospherical surfaces are discussed.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 42(42): 425204, 2009.
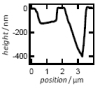 | Local Membrane Mechanics of Pore-Spanning Bilayers
Ingo Mey, Milena Stephan, Eva K. Schmitt, Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131(20): pp. 7031-7039, 2009.
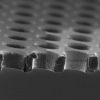 | Elasticity Mapping of Pore-Suspending Native Cell Membranes
Bärbel Lorenz, Ingo Mey, Siegfried Steltenkamp, Tamir Fine, Christina Rommel, Martin Michael Müller, Alexander Maiwald, Joachim Wegener, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
Small, 5(7): pp. 832-838, 2009.
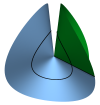 | Conical Defects in Growing Sheets
Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Jemal Guven |
A growing or shrinking disc will adopt a conical shape, its intrinsic geometry characterized by a surplus angle φe at the apex. If growth is slow, the cone will find its equilibrium. Whereas this is trivial if φe≤0, the disc can fold into one of a discrete infinite number of states if φe is positive. We construct these states in the regime where bending dominates, determine their energies and how stress is distributed in them. For each state a critical value of φe is identified beyond which the cone touches itself. Before this occurs, all states are stable; the ground state has twofold symmetry.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 101(15): 156104, 2008. See also arXiv:0807.1814.
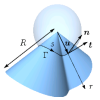 | How paper folds: bending with local constraints
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 41(5): 055203, 2008. See also arXiv:0712.0978.
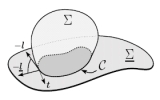 | Contact lines for fluid surface adhesion
Markus Deserno, Martin Michael Müller, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011605, 2007. See also cond-mat/0703019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
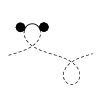 | Balancing torques in membrane-mediated interactions: Exact results and
numerical illustrations
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011921, 2007. See also cond-mat/0702340.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated
interactions
Benedict J. Reynwar, Gregoria Illya, Vagelis A. Harmandaris, Martin Michael Müller, Kurt Kremer, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Nature 447(7143): pp. 461-464, 2007.
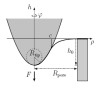 | How to determine local elastic properties of lipid bilayer membranes
from atomic-force-microscope measurements: A theoretical analysis
Davood Norouzi, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 74(6): 061914, 2006. See also cond-mat/0602662.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Mechanical Properties of Pore-Spanning Lipid Bilayers Probed by Atomic Force Microscopy
Siegfried Steltenkamp, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Christian Hennesthal, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
Biophys. J., 91(1): pp. 217-226, 2006.
 | Interface mediated interactions between particles -- a geometrical approach
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 72(6): 061407, 2005. See also cond-mat/0506019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
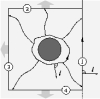 | Geometry of surface-mediated interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 69(3): pp. 482-488, 2005. See also cond-mat/0409043.
2. Books
-
New Trends in the Physics and Mechanics of Biological Systems
Lecture Notes of the Les Houches Summer School, vol. 92 (Oxford University Press, 2011),
edited by Martine Ben Amar, Alain Goriely, Martin Michael Müller and Leticia Cugliandolo.
Chapter 9:
The physics of the cell membrane
Martin Michael Müller and Martine Ben Amar.
3. Theses
-
Theoretical examinations of interface mediated interactions between colloidal particles,
diploma thesis (2004).
-
Theoretical studies of fluid membrane mechanics, dissertation (2007).
-
Symmetry breaking in bioelasticity, habilitation thesis (2015).
|


